JavaScript基础汇总
JS 类型
基本类型
- undefined | null
- String | Number | Boolean
- Symbol 「ECMAScript 2015(ES6第六版)」
- Bigint「es10」
复杂类型
- Object
- Array,Date,RegExp,Function
- 基本包装类型
- Boolean,Number,String
- 单体内置对象
- Global,Math
区别
两种类型的区别是:存储位置不同;
- 值类型存储在栈(stack)中,占空间小、大小固定,属于被频繁使用数据,所以放入栈中存储;
- 引用类型存储在堆(heap)中,占据空间大、大小不固定。如果存在栈中,影响程序运行性能;引用类型在栈中存储了指针,该指针指向堆中该实体的起始地址。当解释器寻找引用值时,会首先检索其在栈中的地址,取得地址后从堆中获得实体。
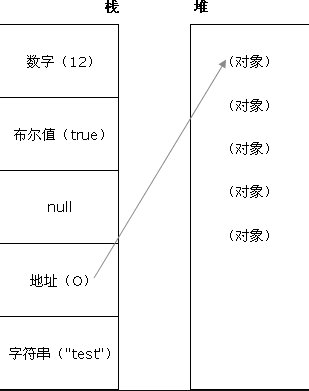
- 栈(stack):是栈内存的简称,栈是自动分配相对固定大小的内存空间,并由系统自动释放,栈数据结构遵循FILO(first in last out)先进后出的原则
- 记忆:类比浏览器 history 先进后出
- 堆(heap):是堆内存的简称,堆是动态分配内存,内存大小不固定,也不会自动释放,堆数据结构是一种无序的树状结构
JS 类型检测
typeof 检测某个值是什么类型
- 8 种返回值
- undefined
- string | number | boolean
- symbol | bigint
- function
- object(包含 array、null)
- typeof 返回的值是字符串类型
- typeof 一个不存在(未定义)的值,不报错,返回字符串
"undefined"
jsx
console.log(typeof [] === 'object'); // true
console.log(typeof null === 'object'); // true
console.log(typeof(undefined)); // undefined
console.log(typeof(NaN)); // numberjsx
console.log( typeof(1 - "1") ) // number
console.log( typeof("1" - "1") ) // number
console.log(a) // Uncaught ReferenceError: a is not defined.
console.log( typeof(a) ) // undefinedjsx
console.log( typeof(typeof(a)) ) // string; hint: typeof() 返回的是字符串instanceof 检测构造函数的 prototype 属性是否出现在某个实例对象的原型链上
- 要检测的对象 instanceof 某个构造函数
jsx
function Car(make, model, year) {
this.make = make;
this.model = model;
}
var auto = new Car('Honda', 'Accord');
console.log(auto instanceof Car);
// expected output: true
console.log(auto instanceof Object);
// expected output: trueundefined
- undefined 既是一个原始数据类型,也是一个原始值数据
- undefined 是全局对象上的一个属性
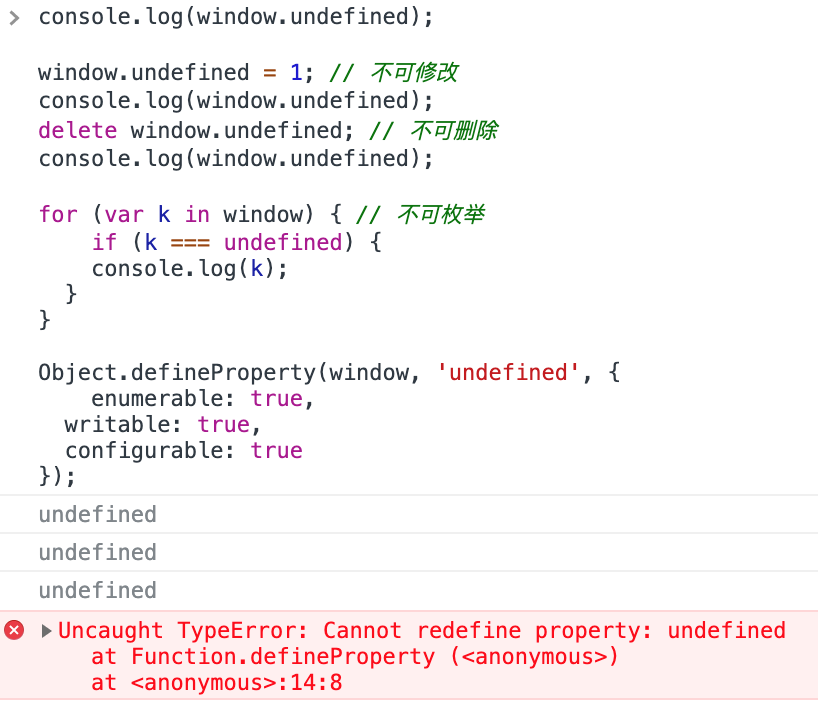
window.undefined- 全局下,undefined 不可重新赋值,不可写,不可删除,不可枚举,不可重新定义
null == undefined- 局部作用域下 undefined 可以当做变量使用
- void(0) 返回 undefined
jsx
console.log(window.undefined);
window.undefined = 1; // 不可修改
console.log(window.undefined);
delete window.undefined; // 不可删除
console.log(window.undefined);
for (var k in window) { // 不可枚举
if (k === undefined) {
console.log(k);
}
}
Object.defineProperty(window, 'undefined', {
enumerable: true,
writable: true,
configurable: true
});
jsx
function test() {
// undefined 不是 JS 的保留字和关键字
var undefined = 1;
console.log(undefined);
console.log(window.undefined === void(100));
console.log(undefined === void(12));
}
test();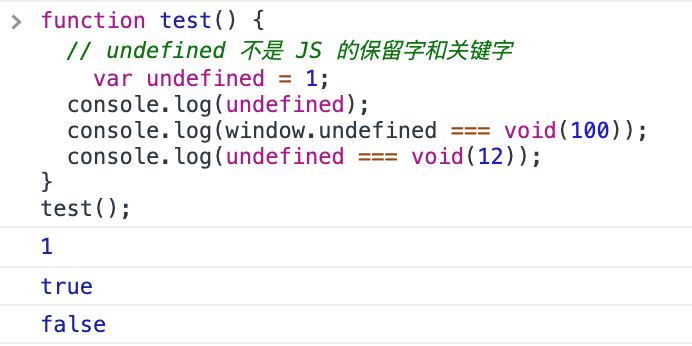
拓展
- 在实际开发过程中会使用
if(xx == null)来判断变量 xx 是否为undefined和null,这样可以更加简洁。(在目前最新的语法中??就是只针对undefined和null做判断处理的,如let a = xx ?? 123) - 使用引用类型时在数据不使用的时候赋值为
null,这样可以避免内存泄漏
jsx
let a = undefined;
let x = a ?? 123;
console.log(x); // 123jsx
let a = null;
let x = a ?? 123;
console.log(x); // 123jsx
// 非 undefined 或 null,则不处理
let a = 0 ?? 999;
console.log(a); // 0JavaScript最大安全数字与最小安全数字
jsx
console.log(Number.MAX_SAFE_INTEGER)
// 9007199254740991
console.log(Number.MIN_SAFE_INTEGER)
// -9007199254740991控制流程 & 表达式与运算符
switch
注意点
- 别忘了写 break,否则会导致 case 穿透现象
- switch 会将 表达式的值 与 case子句 比较判断(
===比较) - switch 是 分支匹配机制(重点:值匹配)
- if (范围匹配)
jsx
function test(c) {
switch(c) {
case c > 90: // 会这样比较 100 === (100 > 90) 也就是 100 === true 比较,结果是 false
console.log(1);
break;
case c > 60:
console.log(2);
break;
default:
console.log(3);
break;
}
}
test(100); // 3
console.log(100 === (100 > 90)); // false三目运算符(条件运算符)
jsx
var str = 89 > 9 ?
'89' > '9' ?
'通过了' :
'内层未通过'
: '外层未通过'; // '内层未通过'
console.log(str);更多
更多 JavaScript 基础请点击此处查看
