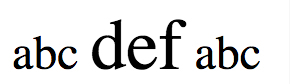如何居中 div?
行内元素水平居中
1
2
3
| #container {
text-align: center;
}
|
单个 div(块级元素)水平居中
1
2
3
4
| #center {
width: 200px;
margin: 0 auto;
}
|
多个 div 水平居中
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
|
#container {
text-align: center;
}
#center {
display: inline-block;
}
#container {
justify-content: center;
display: flex;
}
|
绝对定位的 div 居中(已知宽高)
子绝父相 + margin
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
| #center {
position: absolute;
width: 300px;
height: 300px;
margin: auto;
top: 0;
left: 0;
bottom: 0;
right: 0;
background-color: pink;
}
|
子绝父相 + 负边距
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
| #center {
position: absolute;
width: 500px;
height: 300px;
top: 50%;
left: 50%;
margin: -150px 0 0 -250px;
background-color: pink;
}
|
当被居中的元素是 inline or inline-block 元素
1
2
3
4
5
| #container {
display: table-cell;
text-align: center;
vertical-align: middle;
}
|
任意元素(未知宽高)
子绝父相 + translate
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
| #container {
position: relative;
}
#center {
position: absolute;
top: 50%;
left: 50%;
transform: translate(-50%, -50%);
}
|
flex(需考虑兼容性)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
| #container {
display: flex;
display: -webkit-flex;
align-items: center;
justify-content: center;
}
#center {
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: pink;
}
|
用纯 CSS 创建一个三角形的原理是什么?
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
|
#demo {
width: 0;
height: 0;
border-width: 20px;
border-style: solid;
border-color: transparent transparent red transparent;
}
|
css 多列等高如何实现?
原理
利用 padding-bottom|margin-bottom 正负值相抵;
设置父容器设置超出隐藏(overflow:hidden),这样子父容器的高度就还是它里面的列没有设定 padding-bottom 时的高度, 当它里面的任一列高度增加了,则父容器的高度被撑到里面最高那列的高度, 其他比这列矮的列则会用它们的 padding-bottom 来补偿这部分高度差。
因为背景是可以用在 padding 占用的空间里的,而且边框也是跟随 padding 变化的,所以就成功的完成了一个障眼法。
实现
HTML
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
| <ul class="Article">
<li class="js-equalheight">
<p>
一家将客户利益置于首位的经纪商,
为客户提供专业的交易工具一家将客户利益置于首位的经纪商
</p>
</li>
<li class="js-equalheight">
<p>一家将客户利益置于首位的经纪商,为客户提供专业的交易工具</p>
</li>
<li class="js-equalheight">
<p>一家将客户利益置于首位的经纪商</p>
</li>
</ul>
|
CSS
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
| .Article {
overflow: hidden;
}
.Article > li {
float: left;
margin: 0 10px -9999px 0;
padding-bottom: 9999px;
background: #4577dc;
width: 200px;
color: #fff;
}
.Article > li > p {
padding: 10px;
}
|
css div 垂直水平居中,并完成 div 高度永远是宽度的一半(宽度可以不指定)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
| <!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<title>Document</title>
<style>
* {
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
}
html,
body {
width: 100%;
height: 100%;
}
.outer {
width: 400px;
height: 100%;
background: blue;
margin: 0 auto;
display: flex;
align-items: center;
}
.inner {
position: relative;
width: 100%;
height: 0;
padding-bottom: 50%;
background: red;
}
.box {
position: absolute;
width: 100%;
height: 100%;
display: flex;
justify-content: center;
align-items: center;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="outer">
<div class="inner">
<div class="box">hello</div>
</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
|
来源:https://github.com/cttin/cttin.github.io/issues/2
有一个高度自适应的 div ,里面有两个 div ,一个高度 100px ,希望另一个填满剩下的高度。
HTML
1
2
3
4
5
6
| <body>
<div class="outer">
<div class="A"></div>
<div class="B"></div>
</div>
</body>
|
CSS
方案 1
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
| .A {
height: 100px;
background-color: pink;
}
.B {
background-color: blue;
height: calc(100vh - 100px);
}
|
方案 2
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
|
.outer {
height: 100vh;
padding: 100px 0 0;
box-sizing: border-box;
background-color: pink;
}
.A {
height: 100px;
margin: -100px 0 0;
background: #bbe8f2;
}
.B {
height: 100%;
background: #d9c666;
}
|
方案 3
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
| .outer {
height: 100vh;
padding: 100px 0 0;
box-sizing: border-box;
position: relative;
}
.A {
height: 100px;
background: #bbe8f2;
position: absolute;
top: 0;
left: 0;
width: 100%;
}
.B {
height: 100%;
background: #d9c666;
}
|
方案 4
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
| .outer {
height: 100vh;
position: relative;
}
.A {
height: 100px;
background: #bbe8f2;
}
.B {
background: #d9c666;
width: 100%;
position: absolute;
top: 100px;
left: 0;
bottom: 0;
}
|
方案 5
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
| .outer {
height: 100vh;
background: red;
display: flex;
display: -webkit-flex;
flex-direction: column;
-webkit-flex-direction: row;
}
.A {
width: 100%;
height: 100px;
background: green;
}
.B {
background: blue;
flex: 1;
}
|
rem 布局知道吗?原理是什么?
rem 是个相对单位,相对的是 html 根元素的 font-size 大小。这样一来我们就可以通过 html 上的字体大小来控制页面上所有以 rem 为单位的元素尺寸。
示例代码
例如在 vue 项目的 index.html 页中动态计算根元素字体大小
index.html
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
| <!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8" />
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge" />
<meta
name="viewport"
content="width=device-width,initial-scale=1.0,maximum-scale=1.0,minimum-scale=1.0,user-scalable=no"
/>
...
</head>
<body>
<noscript>...</noscript>
<div id="app"></div>
<script>
(function (doc, win) {
const docEl = doc.documentElement;
const resizeEvt =
'orientationchange' in window ? 'orientationchange' : 'resize';
const recalc = () => {
const clientWidth = docEl.clientWidth;
docEl.style.fontSize = clientWidth / 10 + 'px';
};
if (!doc.addEventListener) return;
win.addEventListener(resizeEvt, recalc, false);
doc.addEventListener('DOMContentLoaded', recalc, false);
recalc();
})(document, window);
</script>
</body>
</html>
|
然后利用 css 预处理器定义一个 mixin 函数(下方用的 stylus),用来将设计稿上的 px 转为对应的 rem 值
计算公式为:
页面元素的 rem 值 = 设计稿元素值(px)/(屏幕宽度 / 划分的份数)
mixin.stylus
1
2
3
4
|
px2rem(designpx)
$rem = 750 / 10;
return (designpx / $rem)rem
|
最后在 css 中使用
某 vue 组件的 style 标签中
1
2
3
4
|
header
width px2rem(750)
height px2rem(100)
|
rem 布局的优缺点
优点:
能维持能整体的布局效果,移动端兼容性好,不用写多个 css 代码,而且还可以利用@media 进行优化。
缺点:
开头要引入一段 js 代码,单位都要改成 rem( font-size 可以用 px ),计算 rem 比较麻烦(可以引用预处理器,但是增加了编译过程,相对麻烦了点)。PC 和 Mobile 要分开。
参考:
慎用 em 的原因
em 会叠加计算。在这个机制下太容易犯错了,因为你不知道这段css指定的字号具体是多少。
HTML
1
2
3
4
5
| <span>
abc
<span>def</span>
abc
</span>
|
CSS
1
2
3
| span {
font-size: 1.5em;
}
|
实际效果:
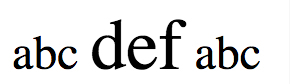
先要搞清楚 em 的计算原理,它是根据当前元素的字号按比例计算的。
外层 span 的字号是 16px(浏览器默认值),所以 1.5em 之后是 24px 。由于字号是继承的,导致内层 span 的字号继承过来是 24px ,再经过 1.5em 之后就成了 36px 。
所以,就算要用 em 的话,尽量不要用在继承属性(font-size)上,除非你真的清楚你在做什么!
两列布局(左列定宽,右列自适应)
HTML
1
2
3
4
| <body>
<div id="left">左列定宽</div>
<div id="right">右列自适应</div>
</body>
|
1. 利用 float + margin
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
| #left {
background-color: #f00;
float: left;
width: 100px;
height: 500px;
}
#right {
background-color: #0f0;
height: 500px;
margin-left: 100px;
}
原理:#left左浮动,脱离文档流,#right为了不被#left挡住,
设置margin-left大于等于#left的宽度达到视觉上的两栏布局
|
2. 使用 float + overflow(触发 bfc)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
| #left {
background-color: #f00;
float: left;
width: 100px;
height: 500px;
}
#right {
background-color: #0f0;
height: 500px;
overflow: hidden;
}
原理:#left左浮动,#right触发bfc达到自适应
|
3. 使用 table 实现
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
| #parent {
width: 100%;
display: table;
height: 500px;
}
#left {
width: 100px;
background-color: #f00;
}
#right {
background-color: #0f0;
}
#left,
#right {
display: table-cell;
}
|
4. 使用 position 实现
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
| #parent {
position: relative;
}
#left {
position: absolute;
top: 0;
left: 0;
background-color: #f00;
width: 100px;
height: 500px;
}
#right {
position: absolute;
top: 0;
left: 100px;
right: 0;
background-color: #0f0;
height: 500px;
}
|
5. 使用 flex 实现
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
| #parent {
width: 100%;
height: 500px;
display: flex;
}
#left {
width: 100px;
background-color: #f00;
}
#right {
flex: 1;
background-color: #0f0;
}
|
两列布局(一列不定宽,一列自适应)
1. float + overflow
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
| #left {
margin-right: 10px;
float: left;
height: 500px;
background-color: #f00;
}
#right {
overflow: hidden;
height: 500px;
background-color: #0f0;
}
原理:#left不设宽度左浮动,#right触发 bfc 达到自适应
|
2. flex 布局
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
| #parent {
display: flex;
}
#left {
margin-right: 10px;
height: 500px;
background-color: #f00;
}
#right {
height: 500px;
background-color: #0f0;
flex: 1;
}
|
三列布局(左中定宽,右侧自适应)
HTML
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| <body>
<div id="parent">
<div id="left">左列定宽</div>
<div id="center">中间定宽</div>
<div id="right">右列自适应</div>
</div>
</body>
|
1. float + margin
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
| #parent {
min-width: 310px;
}
#left {
margin-right: 10px;
float: left;
width: 100px;
height: 500px;
background-color: #f00;
}
#center {
float: left;
width: 200px;
height: 500px;
background-color: #eeff2b;
}
#right {
margin-left: 320px;
height: 500px;
background-color: #0f0;
}
|
2. float + overflow
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
| #parent {
min-width: 320px;
}
#left {
margin-right: 10px;
float: left;
width: 100px;
height: 500px;
background-color: #f00;
}
#center {
margin-right: 10px;
float: left;
width: 200px;
height: 500px;
background-color: #eeff2b;
}
#right {
overflow: hidden;
height: 500px;
background-color: #0f0;
}
|
3. 利用 position
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
| #parent {
position: relative;
}
#left {
position: absolute;
top: 0;
left: 0;
width: 100px;
height: 500px;
background-color: #f00;
}
#center {
position: absolute;
left: 100px;
top: 0;
width: 200px;
height: 500px;
background-color: #eeff2b;
}
#right {
position: absolute;
left: 300px;
top: 0;
right: 0;
height: 500px;
background-color: #0f0;
}
|
4. 利用 table
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
| #parent {
width: 100%;
height: 520px;
margin: -10px 0;
display: table;
border-spacing: 10px;
}
#left {
display: table-cell;
width: 100px;
background-color: #f00;
}
#center {
display: table-cell;
width: 200px;
background-color: #eeff2b;
}
#right {
display: table-cell;
background-color: #0f0;
}
|
5. 利用 flex
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
| #parent {
height: 500px;
display: flex;
}
#left {
margin-right: 10px;
width: 100px;
background-color: #f00;
}
#center {
margin-right: 10px;
width: 200px;
background-color: #eeff2b;
}
#right {
flex: 1;
background-color: #0f0;
}
|
三列布局(两侧定宽,中间自适应)
圣杯布局 详解
HTML
1
2
3
4
5
6
| <div class="container">
<div class="center">中间</div>
<div class="left">左边</div>
<div class="right">右边</div>
</div>
|
CSS
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
| .container {
height: 500px;
min-width: 400px;
padding: 0 100px 0 150px;
background-color: gray;
}
.left {
margin-left: -100%;
position: relative;
left: -150px;
height: 100%;
float: left;
width: 150px;
background-color: rgba(233, 233, 0, 0.2);
}
.center {
height: 100%;
width: 100%;
float: left;
background-color: rgba(165, 12, 23, 0.4);
}
.right {
margin-right: -100px;
height: 100%;
width: 100px;
float: left;
background-color: green;
}
|
双飞翼布局方法 详情
HTML
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| <div class="container">
<div class="center">
<div>中间</div>
</div>
<div class="left">左边</div>
<div class="right">右边</div>
</div>
|
CSS
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
| .container {
width: 100%;
height: 500px;
background-color: gray;
}
.left {
width: 100px;
margin-left: -100%;
background-color: rgba(233, 233, 0, 0.2);
}
.center {
width: 100%;
background-color: rgba(165, 12, 23, 0.4);
}
.center div {
margin: 0 150px 0 100px;
}
.right {
width: 150px;
margin-left: -150px;
background-color: green;
}
.left,
.center,
.right {
height: 100%;
float: left;
}
|
布局的几种方式
- 伸缩布局 flex
- 流式布局 百分比
- 响应式布局 媒体查询(超小屏设备时:流式布局)
<!- 以上布局共同点:元素只能做到宽度的适配(排除图片)->
- rem 布局 宽度和高度都能做到适配(等比适配)
Flex
flex 布局和传统布局的优势?
该布局模型的目的是提供一种更加高效的方式来对容器中的条目进行布局、对齐和分配空间。
在传统的布局方式中:
- block 布局是把块在垂直方向从上到下依次排列的
- inline 布局则是在水平方向来排列
- flex 弹性盒布局并没有这样内在的方向限制,可以由开发人员自由操作
请解释一下 CSS3 的 Flexbox(弹性盒布局模型),以及适用场景?
该布局模型的目的是提供一种更加高效的方式来对容器中的条目进行布局、对齐和分配空间。
在传统的布局方式中:
- block 布局是把块在垂直方向从上到下依次排列的;
- inline 布局则是在水平方向来排列。
- flex 弹性盒布局并没有这样内在的方向限制,可以由开发人员自由操作。
适用场景:弹性布局适合于移动前端开发,在 Android 和 iOS 上也完美支持。
参考:http://www.w3cplus.com/css3/flexbox-basics.html
flex 是什么属性的缩写
flex 属性是 flex-grow、flex-shrink 和 flex-basis 的简写
如何使用 flex 实现三列等宽布局
父元素 display: flex,子元素 flex: 1
解释
子元素的设置等同于:flex: 1 1 auto
flex 的默认值是:0 1 auto
意思是项目默认有剩余空间也不放大(0),但空间不足会缩小(1)
现在改为了值 1 ,就可以放大了,所以三栏可以平分宽度
阅读:flex 设置成 1 和 auto 有什么区别
如何使用 flex 实现下列布局

HTML
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
| <div id="container">
<div class="box box1">1</div>
<div class="box box2">2</div>
<div class="box box3">3</div>
<div class="box box4">4</div>
<div class="box box5">5</div>
</div>
<p>margin-right: auto</p>
|
CSS
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
| #container {
display: flex;
justify-content: flex-end;
background-color: lightyellow;
}
.box {
display: flex;
align-items: center;
justify-content: center;
height: 50px;
width: 75px;
background-color: springgreen;
border: 1px solid #333;
}
.box1 {
margin-right: auto;
}
p {
width: 100%;
text-align: center;
}
|
摘自:css flex 布局中妙用 margin: auto
如何解决移动端 Retina 屏 1px 像素问题
原理:媒体查询 + 变换缩放
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
| <!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width,initial-scale=1.0" />
<style type="text/css">
* {
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
}
#test {
width: 100%;
height: 1px;
margin-top: 50px;
background: black;
}
@media only screen and (-webkit-device-pixel-ratio: 2) {
#test {
transform: scaleY(0.5);
}
}
@media only screen and (-webkit-device-pixel-ratio: 3) {
#test {
transform: scaleY(0.333333333333333333);
}
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div id="test"></div>
</body>
</html>
|
stylus 实现方案
stylus
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
| copy/* 给 dpr 1.5 的设备设置 0.7 的缩放 */
@media (-webkit-min-device-pixel-ratio: 1.5), (min-device-pixel-ratio: 1.5)
.border1px
&::after
-webkit-transform: scaleY(.7)
transform: scaleY(.7)
/* 给 dpr 2.0 的设备设置 0.5 的缩放 */
@media (-webkit-min-device-pixel-ratio: 2), (min-device-pixel-ratio: 2)
.border1px
&::after
-webkit-transform: scaleY(.5)
transform: scaleY(.5)
/* 给需要1px下边框的元素添加一个伪元素,
使其宽100%;高为用户自定义 */
border1px($color)
position: relative
&:after
display: block
position: absolute
left: 0
bottom: 0
width: 100%
border-top: 1px solid $color
content: ' '
|
html
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
|
<header class="border1px"></header>
<style lang="stylus" scoped>
header
...
border1px(black)
</style>
|
CSS 实现宽度自适应 100%,宽高 16:9 比例的矩形
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
| <style>
.box {
width: 100%;
}
.scale {
width: 100%;
padding-bottom: 56.25%;
height: 0;
position: relative;
}
.item {
width: 100%;
height: 100%;
background-color: #e1e1e1;
position: absolute;
}
</style>
<div class="box">
<div class="scale">
<div class="item">
<img src="" />
</div>
</div>
</div>
|
其它
实现不使用 border 画出 1px 高的线,在不同浏览器的标准模式与怪异模式下都能保持一致的效果。
1
| <div style="height:1px;overflow:hidden;background:red"></div>
|
已知如下代码,如何修改才能让图片宽度为 300px ?注意下面代码不可修改
1
| <img src="1.jpg" style="width:480px!important;" />
|
答案:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
|
<img src="1.jpg" style="width:480px!important; max-width: 300px" />
<img src="1.jpg" style="width:480px!important; transform: scale(0.625, 1);" />
<img src="1.jpg" style="width:480px!important; width:300px!important;" />
<style>
img {
animation: test 0s forwards;
}
@keyframes test {
from {
width: 300px;
}
to {
width: 300px;
}
}
</style>
|
题目来源:Daily-Interview-Question 第 60 题
了解 box-sizing 吗?
box-sizing 属性可以被用来调整这些表现:
content-box 是默认值。如果你设置一个元素的宽为 100px,那么这个元素的内容区会有 100px 宽,并且任何边框和内边距的宽度都会被增加到最后绘制出来的元素宽度中。border-box 告诉浏览器:你想要设置的边框和内边距的值是包含在 width 内的。也就是说,如果你将一个元素的 width 设为 100px,那么这 100px 会包含它的 border 和 padding,内容区的实际宽度是 width 减去(border + padding)的值。大多数情况下,这使得我们更容易地设定一个元素的宽高。