前言
平常写前端项目时,为了更方便的获取“真实”的动态数据,也会新建几个数据库表来作支撑。但每每需要用Node搭建后端服务时,数据库的查询真的让人头疼,难倒不难,就是特别繁琐,即使封装了个查询sql用工具模块,在遇到稍复杂的查询语句时还是得写完整SQL。
我又是个比较懒的人,在经历了几次痛苦折磨后,我开始google有没有谁帮我们解决了数据库表字段与对象之间的关系映射。也就是我们通常所说的 ORM 。经过几番搜索,我找到了 Sequelize 框架。在了解它之前,我们先简单介绍下什么是 ORM :(我知道不少人是不会点击上面链接查看详情的 :))
介绍
ORM
ORM 全称 Object Relational Mapping,翻译成中文就是 对象关系映射 。是对 SQL 查询语句的封装,让我们可以用面向对象的方式操作数据库,来更加优雅的生成安全、可维护的 SQL 代码。说白了,就是通过对象来映射和操作数据库。
Sequelize
而今天的主角 Sequelize 则是一个基于 promise 的 Node.js 异步ORM框架。它能够支持多种数据库,包含但不限于 PostgreSQL, MySQL 和 MSSQL 。
官网地址:http://docs.sequelizejs.com/
github:https://github.com/sequelize/sequelize
使用
起步
在本地新建文件夹,例如 sequelize-demo ,然后在项目根目录下运行命令行命名 npm init -y。运行完该命令后项目tree如下:
接着使用 npm 安装 sequelize:
连接数据库
完成上述步骤以后,我们在根目录下新建一个 app.js 文件来使用 sequelize ,代码如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
|
const Sequelize = require('sequelize');
const sequelize = new Sequelize('数据库名称', '数据库用户名', '数据库密码', {
host: '127.0.0.1',
port: 8889,
dialect: 'mysql',
timezone: '+08:00'
});
try {
sequelize.authenticate();
console.log('数据库连接成功!');
} catch (err) {
console.log('连接失败');
}
|
此时你可以尝试运行 app.js 文件,即在根目录下运行 node app.js 命令。正常情况下你会收到报错信息,类似这样:
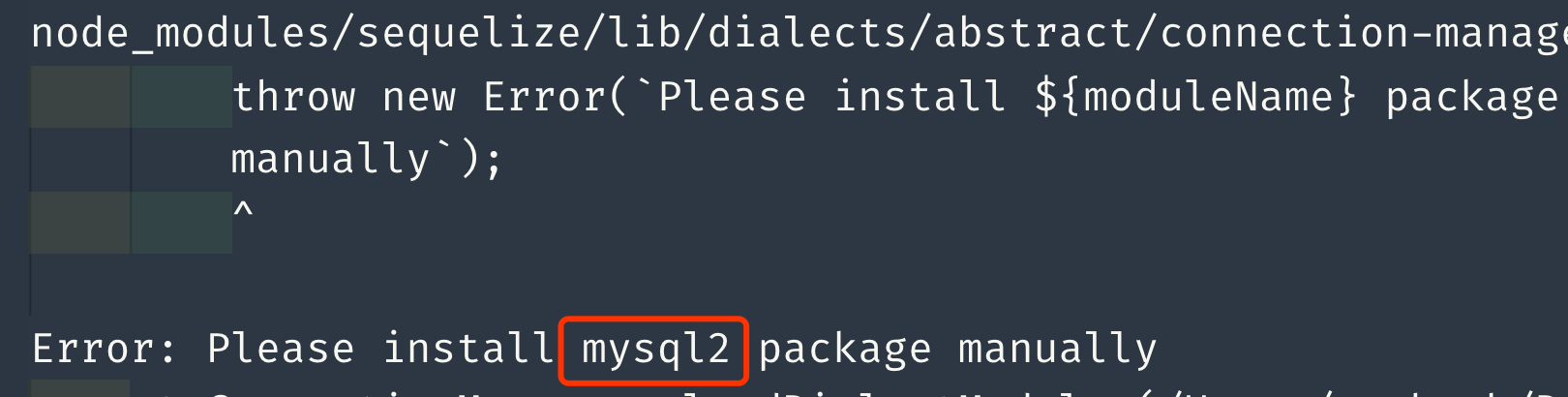
意思是你需要安装 mysql2 ,这是因为 sequelize 虽然依赖了 mysql2 ,但却没有内置安装。所以接下来你得在项目根目录下运行如下代码来安装 mysql2:
安装完毕后再次运行 app.js ,就能连接数据库成功了:
1
2
3
| node app.js
Executing (default): SELECT 1+1 AS result
数据库连接成功!
|
定义模型(Model)
所谓模型,就是用来描述数据库表字段信息的对象,每一个模型对象表示数据库中的一个表,后续对数据库的操作都是用过对应的模型对象来完成的。
接下来我们就要定义数据的模型了。在此之前,你还需要做一些准备工作。以我为例,我在数据库中新建了一个 users 表,表字段和类型如下:
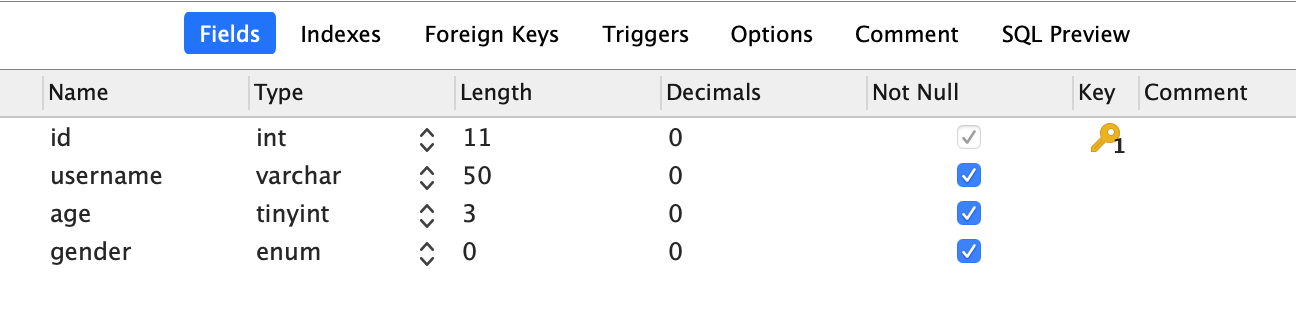
然后定义出对应此表的数据模型:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
|
const UserModel = sequelize.define('User', {
id: {
type: Sequelize.INTEGER(11),
allowNull: false,
autoIncrement: true,
primaryKey: true,
},
username: {
type: Sequelize.STRING(50),
allowNull: false,
defaultValue: '',
},
age: {
type: Sequelize.TINYINT(3),
allowNull: false,
},
gender: {
type: Sequelize.ENUM(['men', 'women', 'other']),
allowNull: false,
defaultValue: 'men',
},
}, {
timestamps: false,
tableName: 'users',
});
|
注意:在定义模型时,字段名称可以和数据库表中的字段名称不相同,但如果你想另起一个别名,则需要在字段信息设置中加入 field 来关联真正的表字段名称。例如:
1
2
3
4
5
| userName: {
type: Sequelize.STRING(50),
allowNull: false,
field: 'username',
},
|
数据查询
查询所有
完成表模型的定义以后,我们就可以通过 findAll 来查询表数据了:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
|
UserModel.findAll().then(users => {
users.forEach(user => {
console.log(user.get('username'));
});
}).catch(err => {
console.log(err);
});
|
写完上面代码后,再次运行 app.js ,你就应该能够查询到数据了~
p.s. 查询之前别忘了在数据库中插入一些数据。
条件查询
除了查询全部数据,我们还可以使用 where 查询指定的数据:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
|
(async function() {
let res = await UserModel.findOne({
where: {
username: '李元芳'
}
})
console.dir(res);
})();
|
而类似大于小于这样的查询会稍显麻烦一点。例如我们来编写查询 users 表中年龄大于某个值的代码:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
| (async function () {
let res = await UserModel.findAll({
where: {
age: {
[Sequelize.Op.gt]: 24,
}
}
})
console.dir(res.map(r => r.get('username')));
})();
|
多条件查询
除了单一条件查询,我们还可以通过嵌套 or 或 and 运算符的集合来生成复杂条件语句。例如我们来查询 年龄小于25 或者 性别为男 的所有数据:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
| (async function () {
let { Op } = Sequelize;
let res = await UserModel.findAll({
where: {
[Op.or]: [
{
age: {
[Sequelize.Op.lt]: 25,
}
},
{
gender: 'men'
}
]
}
})
console.dir(res.map(r => r.get('username')));
})();
|
从上面几组查询语句我们可以看出,where 通常用 attribute: value 键值对获取一个对象,其中 value 可以是匹配等式的数据或其他运算符的键值对象。更多查询语法可在下方链接查询:
查询限制 limit, offset
我们还能限制查询的数量:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| (async () => {
let res = await UserModel.findAll({
limit: 2,
});
console.log(res.map(r => r.get('username')));
})();
|
跳过前2条数据:
1
2
3
4
5
6
| (async () => {
let res = await UserModel.findAll({
offset: 2,
});
console.log(res.map(r => r.get('username')));
})();
|
跳过前2条数据并获取3条:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| (async () => {
let res = await UserModel.findAll({
offset: 2,
limit: 3
});
console.log(res.map(r => r.get('username')));
})();
|
查询排序
我们还可以将查询数据进行排序:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
| (async () => {
let res = await UserModel.findAll({
order: [
['age', 'desc']
]
});
console.log(res.map(r => r.get('username')));
})();
|
查询记录
有些时候我们可能只是想单纯的查询数据表中有多少条数据,这时可以用 count() 方法:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
| (async () => {
let count = await UserModel.count();
console.log(count);
})();
(async () => {
let res = await UserModel.findAndCountAll({
limit: 2,
});
console.log(res);
})();
|
查询结果的格式如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
| {
count: 总记录数,
rows: [
{第一条记录}, {第二条记录}, ...
]
}
|
这个方法对我们为前端提供分页功能很方便,count是符合条件的总记录数,而rows中可以是当前页数下的记录数。
数据增加
既然能查,当然就能往数据库插入数据,在 sequelize 中,插入数据可以用 build 方法:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
|
let wangwu = UserModel.build({
username: '王五',
age: 22,
gender: 'men'
});
wangwu.set('age', 25);
wangwu.save();
|
如果运行后没报错,去数据库刷新表吧,数据已经成功的插入到 users 表了~
数据修改
实际开发中修改数据是再平常不过的了,比如修改一篇博客,更新自己的个人信息… 在 sequelize 中,我们这样修改数据:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
UserModel.findByPk(2).then(user => {
user.set('age', 99);
user.save();
});
|
注意: 在 Sequelize v5 版本以前,通过id查询数据的方法名为 findById ,从 v5 版本开始,更改为 findByPk 。其实想一下这样非常合理,以前的 findById 太主观了,要知道不一定每个表的主键都为 id ,所以更改为 findByPk 后,表示通过主键(Pk -> PrimaryKey)查找,sequelize 会自动通过你在创建表模型时定义的主键字段查找。例如我们一开始在定义 User 模型时,就给 id 字段添加了 primaryKey: true, 属性。
除了 set + update 来更新数据以外,还可以使用 update() 方法做相同的事情:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
| (async function () {
let xiaohong = await UserModel.findByPk(3);
await xiaohong.update({
age: 22,
});
})();
|
数据删除
如果想要删除一条数据,可以使用 destroy 方法:
1
2
3
4
5
6
| (async function () {
let wangwu = await UserModel.findByPk(4);
wangwu.destroy();
})();
|
完整代码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
162
163
164
165
166
167
168
169
170
171
172
173
174
175
176
177
178
179
180
181
182
183
184
185
186
187
188
189
190
191
192
193
194
| const Sequelize = require('sequelize');
const sequelize = new Sequelize("miaov", "root", "root", {
host: "127.0.0.1",
port: 8889,
dialect: "mysql"
});
try {
sequelize.authenticate();
console.log('数据库连接成功!');
} catch (err) {
console.log('连接失败');
}
const UserModel = sequelize.define('User', {
id: {
type: Sequelize.INTEGER(11),
allowNull: false,
autoIncrement: true,
primaryKey: true,
},
username: {
type: Sequelize.STRING(50),
allowNull: false,
defaultValue: '',
},
age: {
type: Sequelize.TINYINT(3),
allowNull: false,
},
gender: {
type: Sequelize.ENUM(['men', 'women', 'other']),
allowNull: false,
defaultValue: 'men',
},
}, {
timestamps: false,
tableName: 'users',
});
(function() {
UserModel.findAll().then(users => {
users.forEach(user => {
console.log(user.get('username'));
});
}).catch(err => {
console.log(err);
});
});
(async function() {
let liyuanfang = UserModel.build({
username: '李元芳',
age: 09,
gender: 'men'
});
liyuanfang.set('age', 25);
await liyuanfang.save();
});
(function() {
UserModel.findByPk(2).then(user => {
user.set('age', 99);
user.save();
});
});
(async function() {
let xiaohong = await UserModel.findByPk(3);
await xiaohong.update({
age: 18
});
});
(async function () {
let wangwu = await UserModel.findByPk(4);
wangwu.destroy();
});
(async function() {
let res = await UserModel.findOne({
where: {
username: '李元芳'
}
})
console.dir(res);
});
(async function () {
let res = await UserModel.findAll({
where: {
age: {
[Sequelize.Op.gt]: 24,
}
}
})
console.dir(res.map(r => r.get('username')));
});
(async function () {
let { Op } = Sequelize;
let res = await UserModel.findAll({
where: {
[Op.or]: [
{
age: {
[Sequelize.Op.lt]: 25,
}
},
{
gender: 'men'
}
]
}
})
console.dir(res.map(r => r.get('username')));
});
(async () => {
let res = await UserModel.findAll({
limit: 2,
});
console.log(res.map(r => r.get('username')));
});
(async () => {
let res = await UserModel.findAll({
offset: 2,
});
console.log(res.map(r => r.get('username')));
});
(async () => {
let res = await UserModel.findAll({
offset: 2,
limit: 3
});
console.log(res.map(r => r.get('username')));
});
(async () => {
let res = await UserModel.findAll({
order: [
['age', 'desc']
]
});
console.log(res.map(r => r.get('username')));
});
(async () => {
let count = await UserModel.count();
console.log(count);
});
(async () => {
let res = await UserModel.findAndCountAll({
limit: 2,
});
console.log(res);
})();
|
版本
安装的 sequelize 和 mysql2 的版本为:
1
2
3
4
| "dependencies": {
"mysql2": "^1.6.5",
"sequelize": "^5.3.1"
}
|
资源


